【印刷可能】 back of head anatomy term 178736-Back of the head anatomy terminology
Crown The Crown refers to the area at the upper back of the skull The Crown begins at the point where the top of the head begins to curve downward to the back of the head and ends at the point just above the Occipital bone It is a semicircular area This article looks at the anatomy of the back, including bones, muscles, and nerves It also covers some common conditions and injuries that can affect the backIn this video we discuss the anatomical directional terms, which is a directional language used to reference points or areas of the human bodyAnatomical dir
Anatomical Terminology
Back of the head anatomy terminology
Back of the head anatomy terminology- Now, there are more directional terms than just toward the front or the back of something We also have the term superior, which means towards the head or above something, and the word inferiorPoor posture If you tend to slouch when you sit or stand, that can strain the muscles in the back of your head, upper back, neck, and jaw It also can put pressure on the nerves in those areas




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jaw It is attached to the spinal column by way of the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, and connected with the trunk of the body by the muscles, blood vessels, and nerves that constitute the neck The term also is used to describe the anterior or fore part ofTo be heading back → auf demHead hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such an
Posterior – Located behind a structure, such as relating to the back side of the human body Prosthesis – An artificial body part such as an artificial leg or arm The term prosthesis is also used to describe some of the implants used in the body such as a hip or knee replacement device Proximal – Nearest the center of the body The muscles of the back categorize into three groups The intrinsic or deep muscles are those muscles that fuse with the vertebral column The second group is the superficial muscles, which help with shoulder and neck movements The final group is the intermediate muscles, which help with the movement of the thoracic cage Only the intrinsic muscles are considered trueStandard Terminology for the Head and Face The appearance of facial morphology varies considerably with facial expression and movement, and depending on the position of the observer and observed person When assessing a feature, the head of the observed person should be held in the Frankfurt horizontal, with the facial and neck muscles relaxed
A common feature most often in the form ofIn medical term, it is called as Occipital neuralgia It is a condition in which the nerves that go from the top of the spinal cord up via the scalp, named the occipital nerves, are swollen or injured And you might feel pain in back of your head at base of your skull and NauseaGlossary of Hat Terms Crown The top portion of the hat;




Anatomical Terminology Anterior Front Of The Animal Ppt Download




Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Taken From Atlas Of Human Anatomy Netter Frank H Amazon Com Books
These help us to communicate the locations of body structures Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for freeAnterior means the front and posterior means the back Your face is anterior to the back of your head Your lower back is posterior to your belly Anterior and PosteriorWebMD's Brain Anatomy Page provides a detailed diagram and definition of the brain including its function, parts, and conditions that affect it Head injuries and strokes may cause epilepsy



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy Physiology




Anatomical Terms Of Location Wikipedia
There are a wide variety of causes of these bumps In addition, each human skull has a natural bump on the back of the head This bump,The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain beneath the occipital lobes It is separated from the cerebrum by the tentorium (fold of dura) is divided into two major parts the right and left cerebral hemispheres The cerebrum is a term often used to describe the entire brain It guides eye and head movements and a person'sHead and Neck Terms and Definitions Head and Neck Equivalent Terms, Definitions, Charts, Tables and Illustrations C000C148, C300C329 (Excludes lymphoma and leukemia – M9590 – 99 and Kaposi sarcoma M9140) Table 1 –Paired Sites Table Instructions Use this table to determine multiple primary status for sites listed in Column 1 Column 1



Directional Terms Course Hero



Head Anatomy Definition Of Head Anatomy By Medical Dictionary
What is the Pain in Back of Head at Base of Skull ? The pain in the back of your head occurs when one or a combination of factors affect your brain The Mayo Clinic says that these factors can be chemical activity in your brain, the nerves of blood vessels surrounding your skull, or the muscles at the back of the head and neck 1 Also, some people are more prone to headaches than others Knowing what causes headachesAnatomical Positions 71 terms jwhidden anatomy terminology list 46 terms Ponydragon OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR French body body parts 33 terms




Head Definition Anatomy Britannica
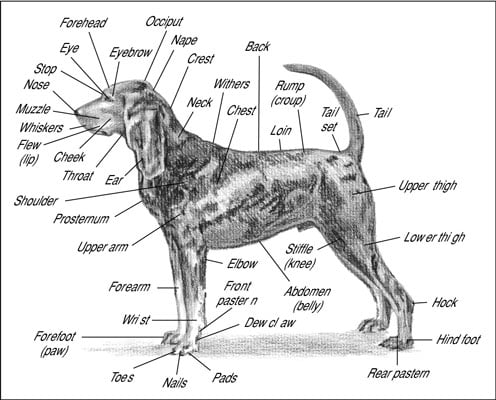



Dog Anatomy From Head To Tail Dummies
The neck refers to the collection of structures that connect the head to the torso It is a complex structure composed of many bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other connective tissues The cervical spine is the bony part of the neck Its primary function is to provide support for the skull, while still allowing for movement It is the most flexible part of theHead (anatomy) synonyms, Head (anatomy) pronunciation, Head (anatomy) translation, English dictionary definition of Head (anatomy) n 1 a The uppermost or forwardmost part of the body of a vertebrate, containing the brain and the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and jaws b head back vi → zurückgehen/fahren;The Organs of the Head include the ear, the eye, the nose and sinuses, the salivary glands, and the oral cavity The ear can be divided in to three sections the external ear, the middle ear, and the inner earThe external ear functions to capture and direct sound waves through the external acoustic meatus to reach the tympanic membrane (ear drum) ) The tympanic membrane marks




Crown Of Head Conditions Injuries And More




Anatomical Terminology Foundations Of Neuroscience
A chicken's head has several parts, as shown in Figure 7 One of the most prominent features on a chicken's head is the comb Figure 8 shows different types of combs A chicken's comb and wattles are red, soft, and warm Chickens do not have external ears as humans do The ears are just openings into the ear canal, and each is protectedThese terms usually come in pairs, with one word meaning a specific direction and the paired word meaning the opposite Let's take a look at some common directional terms Head is superior to the chest Pelvis is inferior to the chest Abdomen is on the ventral side of our body Spine is on the dorsal side of our body Anatomical Directional Terms Anterior In front of, front Posterior After, behind, following, toward the rear Distal Away from, farther from the origin Proximal Near, closer to the origin Dorsal Near the upper surface, toward the back Ventral Toward the bottom, toward the belly Superior Above, over



Drcroes Com




Week 1 Terms Body Tissues Medical Imaging Hbs1hbb Week 1 Terminology Body Tissues And Medical Studocu
Regions of the body are identified using terms such as "occipital" that are more precise than common words and phrases such as "the back of the head" Directional terms such as anterior and posterior are essential for accurately describing the relative locations of body structuresWith a good grasp of foot anatomy it readily becomes apparent which surgical approaches can be used to access various areas of the foot and ankle There are a variety of anatomical structures that make up the anatomy of the foot and ankle (Figure 1) including bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and nervesThe muscles of the head include the tongue, muscles of facial expression, extraocular muscles and muscles of mastication The tongue comprises of intrinsic and extrinsic musclesIt receives motor innervation from the hypoglossal nerve Sensation of the tongue can be divided into taste, and general sensation The muscles of facial expression are located in the subcutaneous tissue



Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions




Anatomy 328 Exam 1 Flashcards Quizlet
Superior and Inferior Anterior/Posterior These two terms indicate the location of anatomy with reference to the front and back;The head, attached to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by the neck muscles When these muscles act unilaterally, the head rotates When they contract bilaterally, the head flexes or extends The major muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid In addition, both muscles workingTreatment The occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the




Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Temple Anatomy Wikipedia
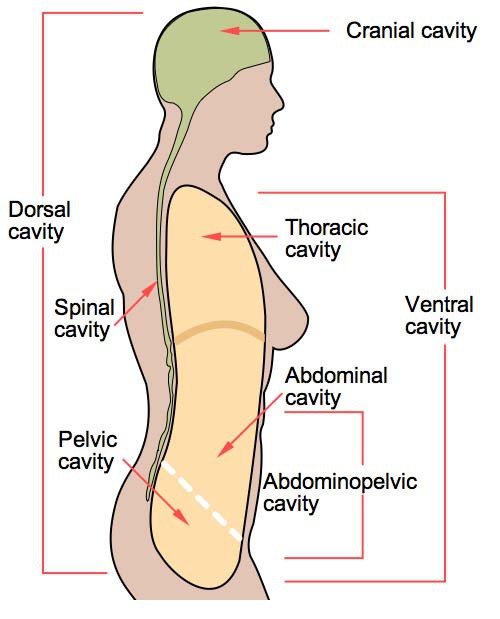
Common Terms Used For Features of Bones (and other aspects of anatomy) Term Description Example Articulations Condyle A rounded knob that articulates with another bone Occipital condyles of skull Facet A smooth, flat, slightly concave or convex articular surface Articular facets of the vertebrae Head1 Body cavities – hollow spaces within the human body that contain internal organs a)The dorsal cavitylocated toward the back of the body, is divided into the cranial cavity (which holds the brain) and vertebral or spinal cavity (which holds the spinal cord) It runs from the back of the head to the small of the back The laryngeal prominence, more commonly known as the Adam's apple , is a noticeable external neck feature It is more prominent in men




Anatomy Terms Illustrated Health Infographics Infographic Health Anatomy Medical Knowledge



17 1 Anatomical Terminology Social Sci Libretexts
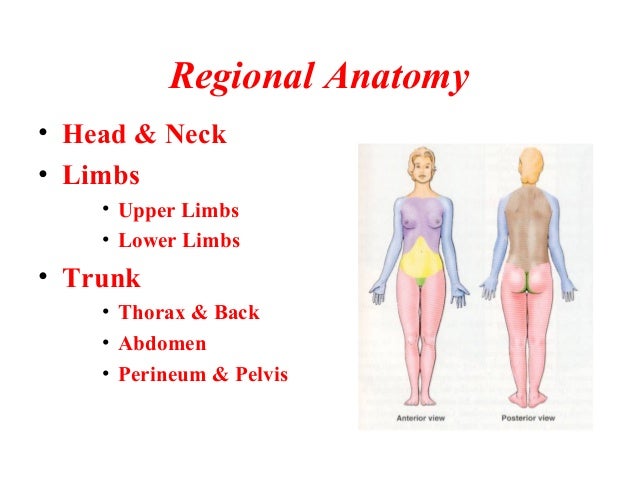
Human head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of masticationThe anatomical regions (shown) compartmentalize the human body Just like on a map, a region refers to a certain area The body is divided into two major portions axial and appendicular The axial body runs right down the center (axis) and consists of everything except the limbs, meaning the head, neck, thorax (chest and back),The area above the brim that sits on your head Tip The uppermost peak of the crown Pinch/Dent Also called the crease, this refers to the indentations made along the front, back, and sides of the crown Hat Band The decorative strip of material encircling a hat, positioned above the brim;
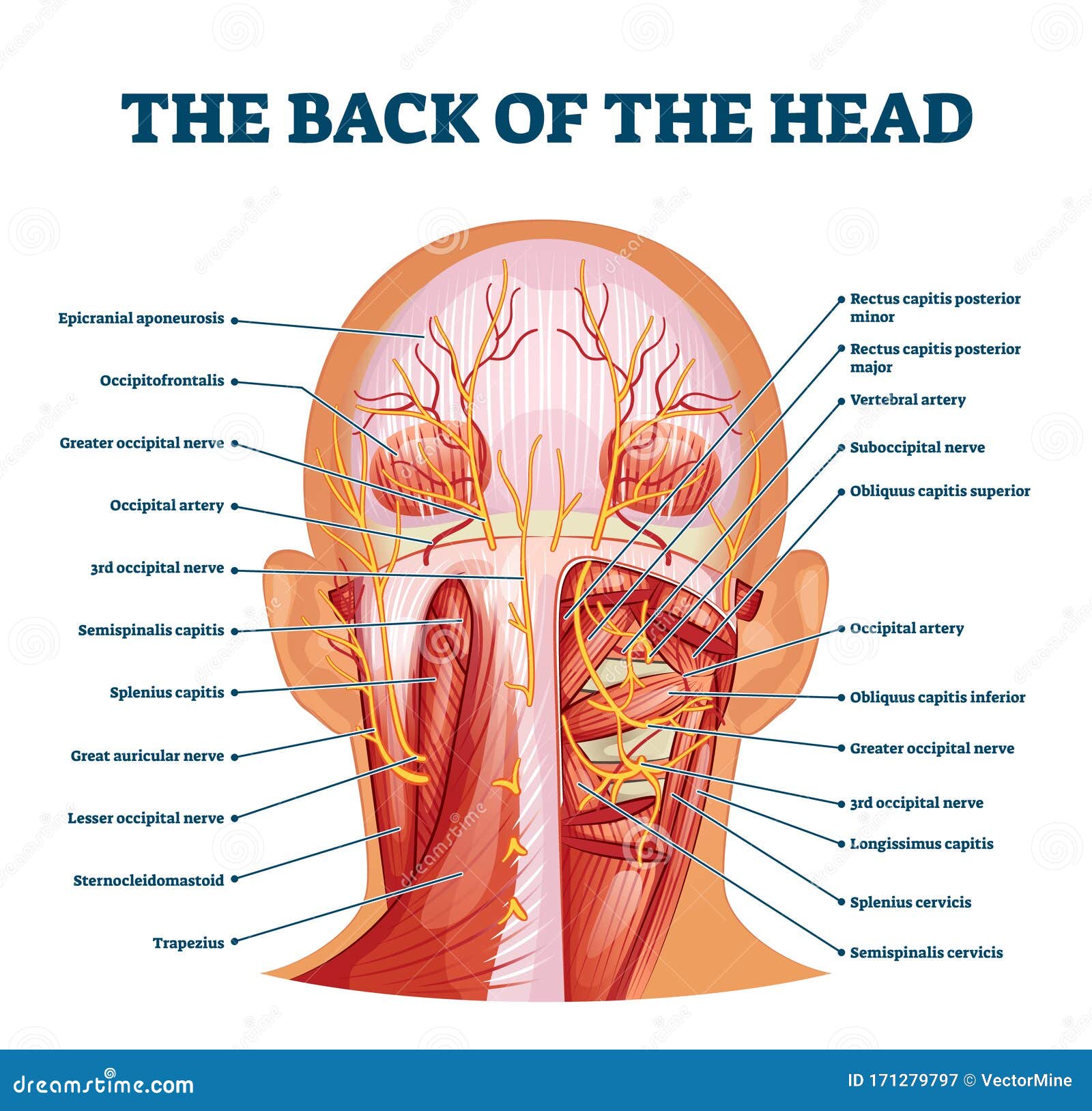



Back Head Diagram Stock Illustrations 366 Back Head Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
It is, therefore, the transitional part of the body between the skull superiorly and the clavicles inferiorly that joins the head to the trunk and limbs It serves as a major conduit for structures passing between themAt the bottom of the brainstem, the medulla is where the brain meets the spinal cord The medulla is essential to survival Functions of the medulla regulate many bodily activities, including heart rhythm, breathing, blood flow, and oxygen and carbon dioxide levels Anatomic orientation terms In anatomy, certain terms are used to denote orientation For example, a structure may be horizontal, as opposed to vertical Some of the terms of anatomic orientation are as follows Anterior The front, as opposed to the posterior Anteroposterior From front to back, as opposed to posteroanterior
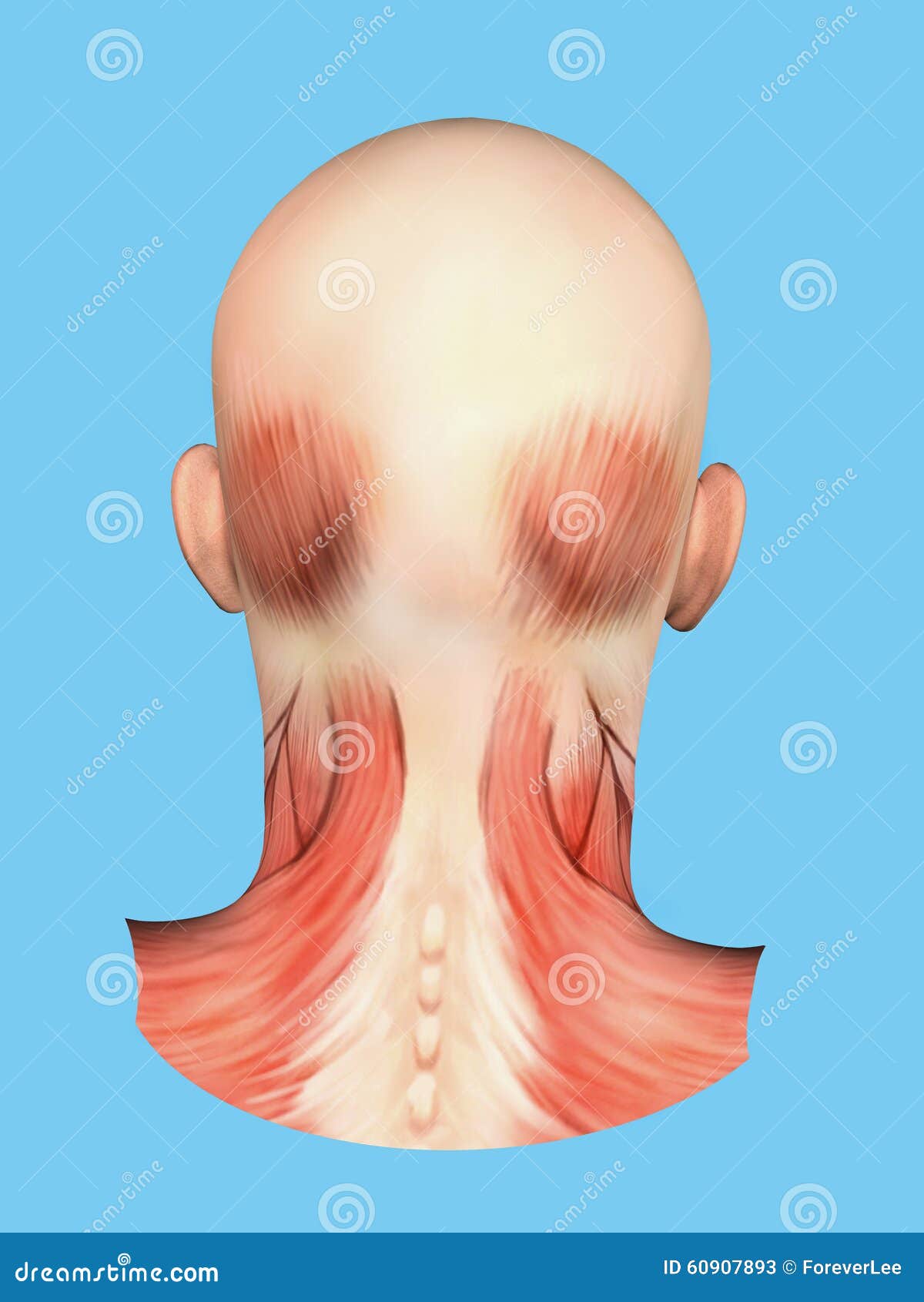



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Anatomical Terminology Foundations Of Neuroscience
In the study of human anatomy the terms "Calvaria, "skullcap", meaning "coming after" Posterior is often used as a technical term in biology and medicine to refer to the back side of things, and is the opposite of anterior, which refers to the front side Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body,




Anatomical Terminology Anatomy And Physiology I
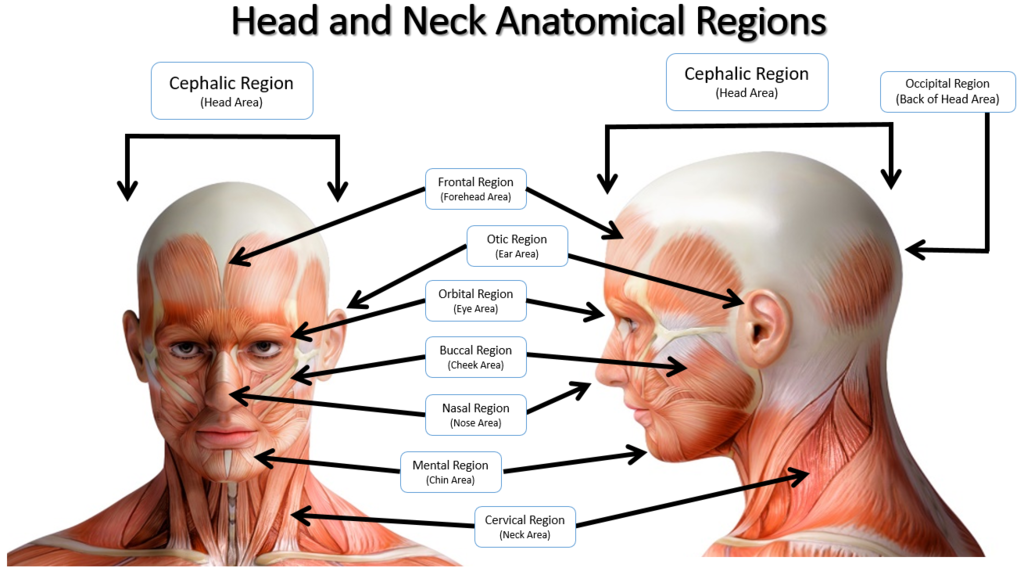



Regional Anatomical Terms For The Head And Neck Area Diagram Quizlet




Anatomical Positions Anatomy And Physiology I Anat 101 Docsity




Regional Terms Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram



1



Lamission Edu
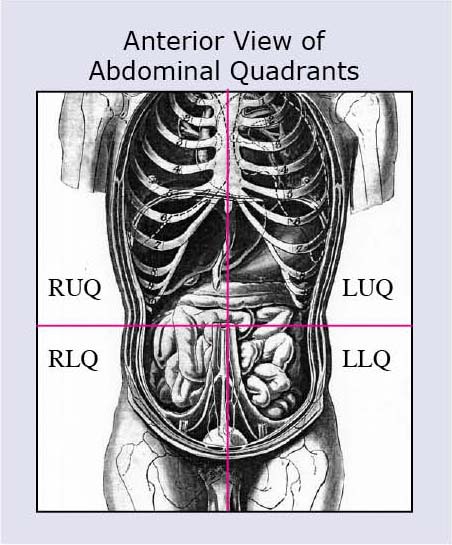



Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions
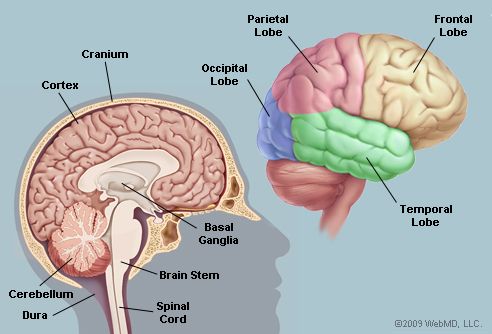



Brain Human Anatomy Picture Function Parts Conditions And More




Anatomy And Physiology Introduction Study Of Anatomy And




Anatomical Terms Of Location Wikipedia
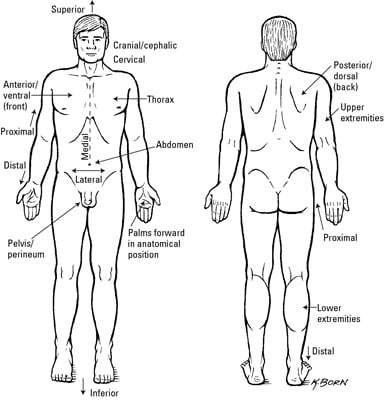



Clinical Anatomy Terms To Describe The Eight Body Regions Dummies




Muscle Anatomy Physiology Health Fitness Training Muscle Bone Neck Muscle Anatomy Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscles Of The Neck
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7841/sternocleido_mastoid.png)



Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub



1




Directional Terms Quiz Anatomy And Physiology
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4479/__diagrams_for_articles_1.jpg)



Brain Orientation Difficulties Directions And Planes Kenhub



Back Of Head Medical Term Clip Art Library
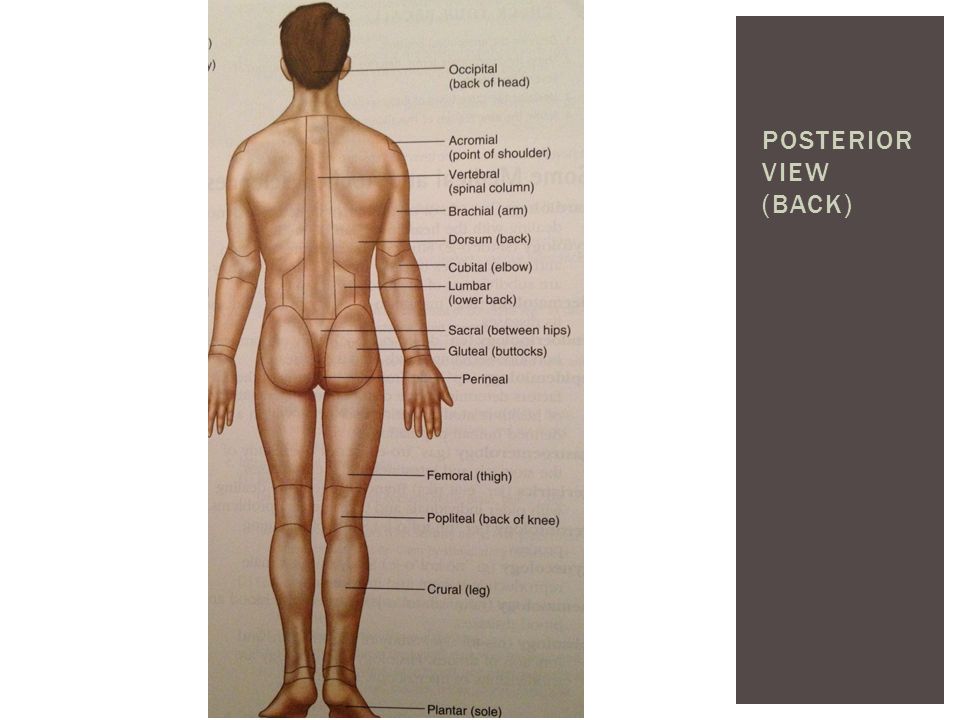



Anatomical Terminology Ppt Download



Anatomy And Physiology Anatomical Position And Directional Terms



Anatomical Terms Wikiradiography



Anatomical Terminology




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
/GettyImages-147219941-56a05efe3df78cafdaa14c5f.jpg)



Superficial Anatomy Of The Back And Core




Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
/anatomical-directional-terms-and-body-planes-373204-01-28f62bf8f2214f71b9d38dfa85beccb5.png)



Anatomical Directional Terms And Body Planes
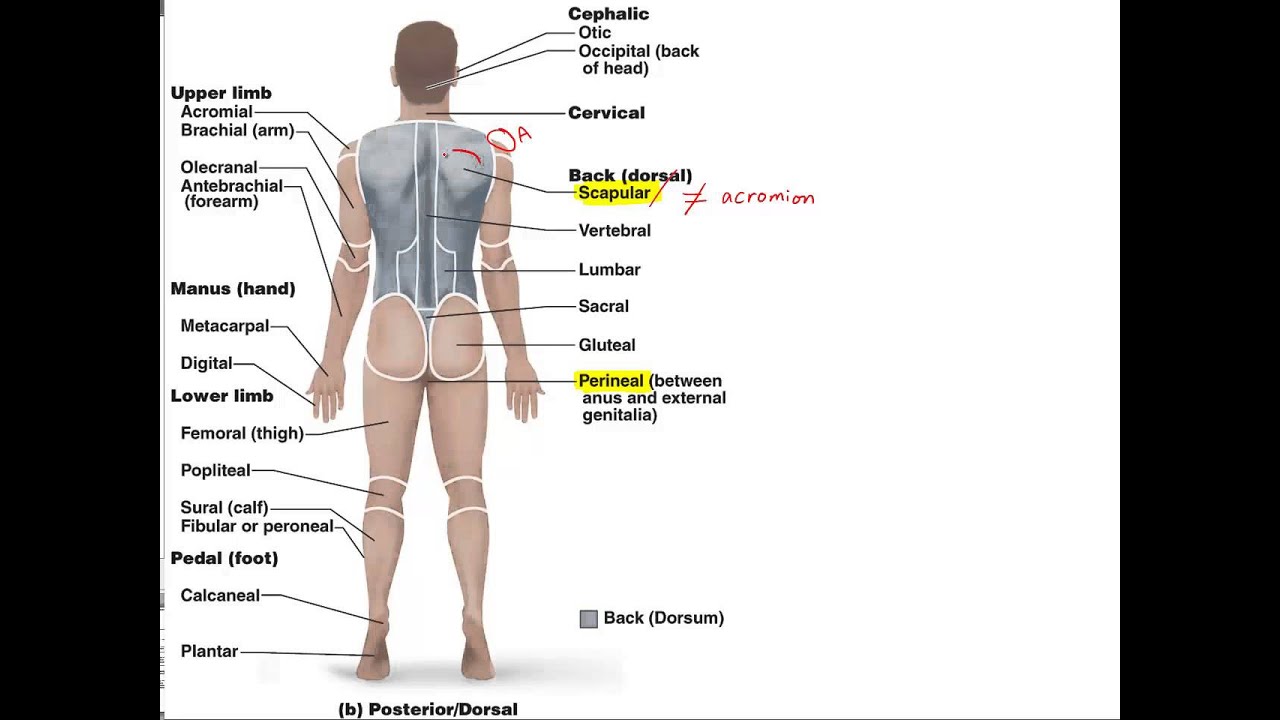



Chapter 1e Anatomical Terminology Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11176/ldiYtHYtg1S9JtrHjGbC6g_Flexion_of_knee.png)



Anatomical Terminology Planes Directions Regions Kenhub




Gross Anatomy Of Muscles Head Neck Back And Chest Flashcards Quizlet




Anatomical Terms Knowledge Amboss




Anatomical Terminology




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Essentials Of Human Anatomy Introduction Chapter 1 Dr
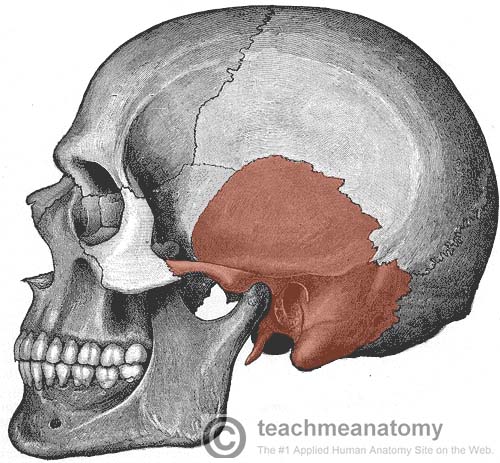



The Temporal Bone Parts Fractures Teachmeanatomy




Language Of Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Terminology Study Human Body Anatomy
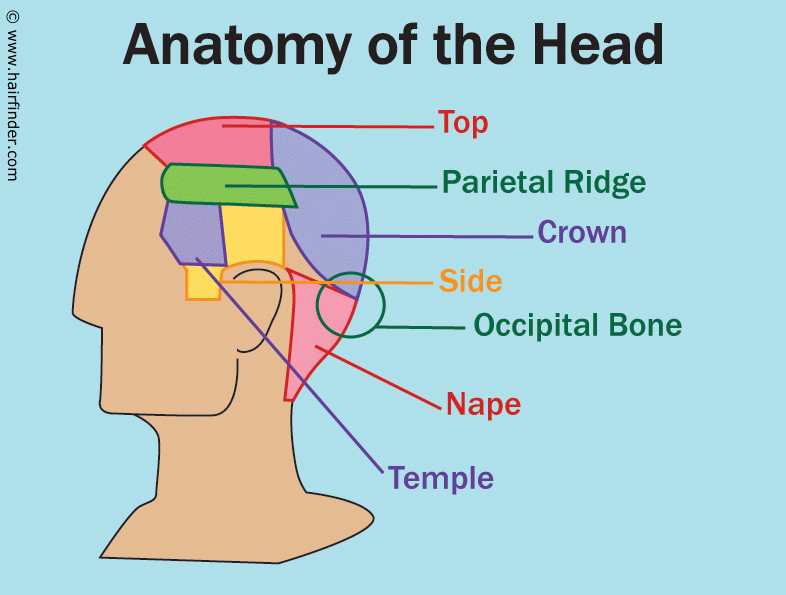



Anatomy Of The Head And The References Used For The Areas Of The Head In Haircuts And Haircutting
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11182/regional-anatomy-of-thorax-and-abdomen_english.jpg)



Anatomical Terminology Planes Directions Regions Kenhub




Regional Anatomy Quiz Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Anatomical Terminology Worksheet Tchs
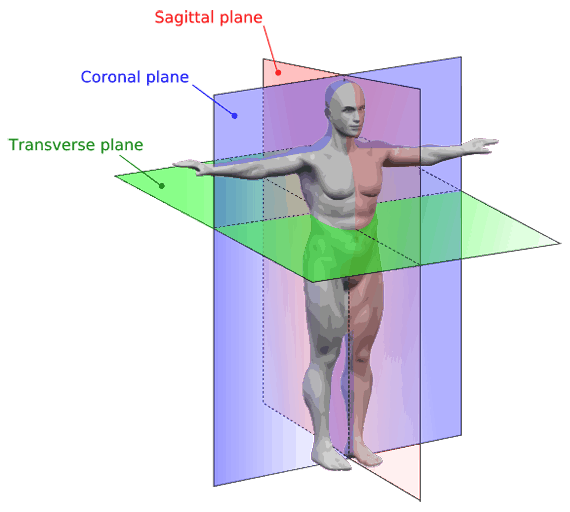



Anatomical Terms Meaning Anatomy Regions Planes Areas Directions
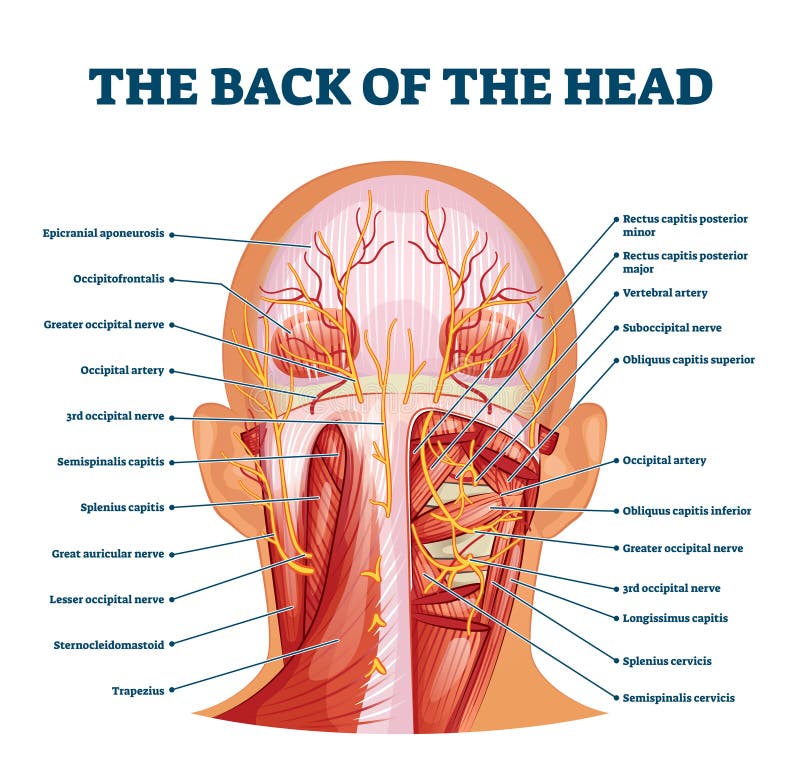



Back Head Vector Stock Illustrations 10 396 Back Head Vector Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Introduction To Human Anatomy Physiology Ppt Video Online Download
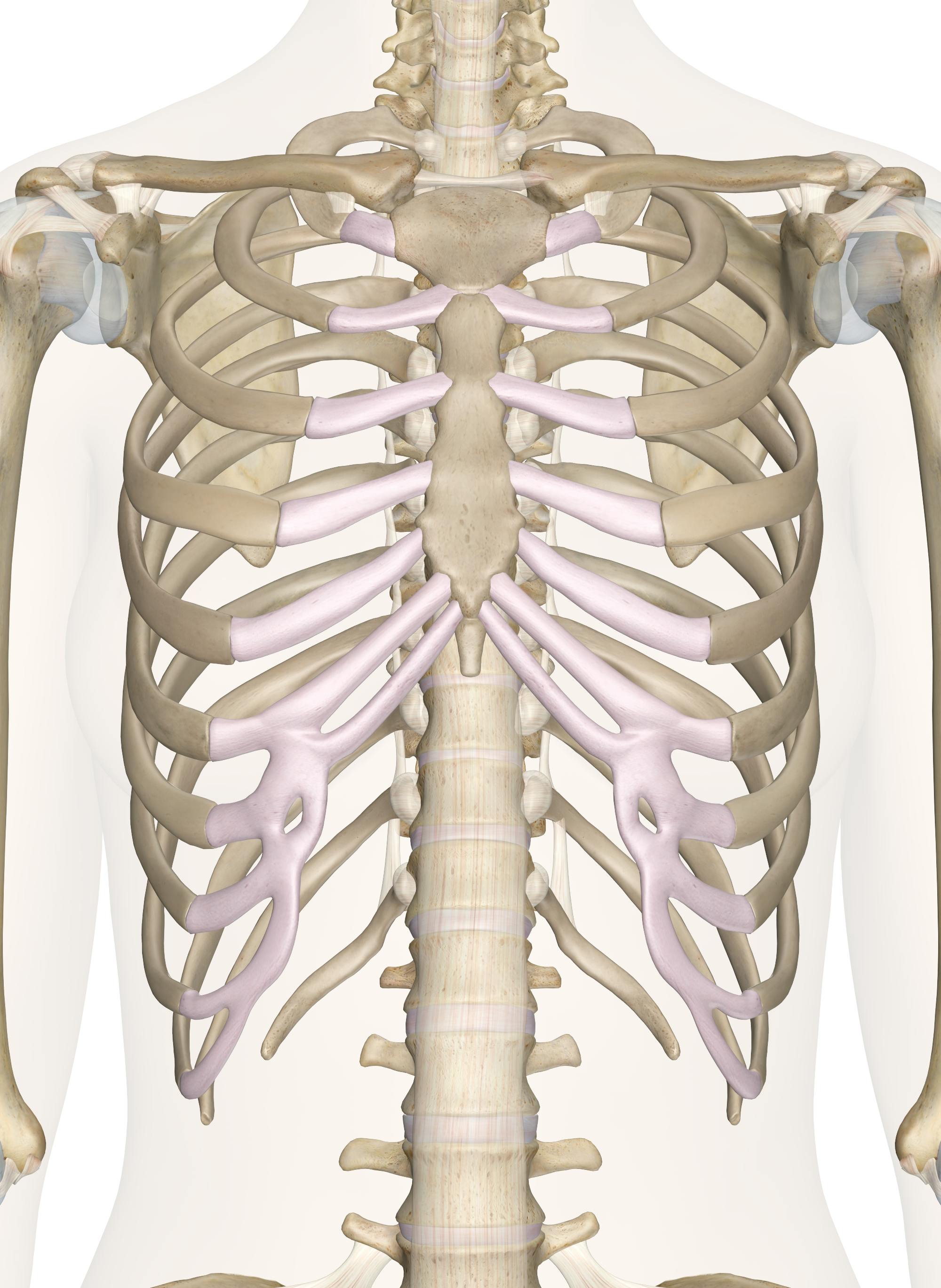



Bones Of The Chest And Upper Back
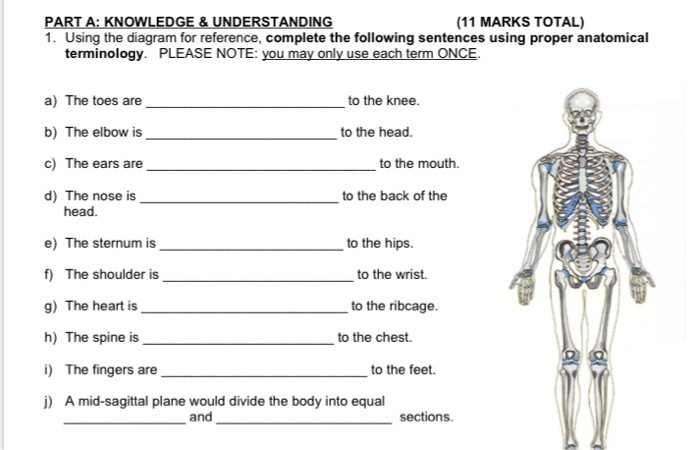



Solved Part A Knowledge Understanding 11 Marks Total 1 Chegg Com
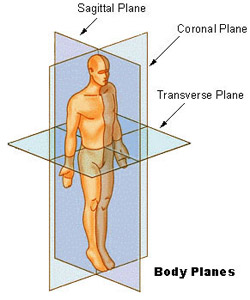



Seer Training Anatomical Terminology
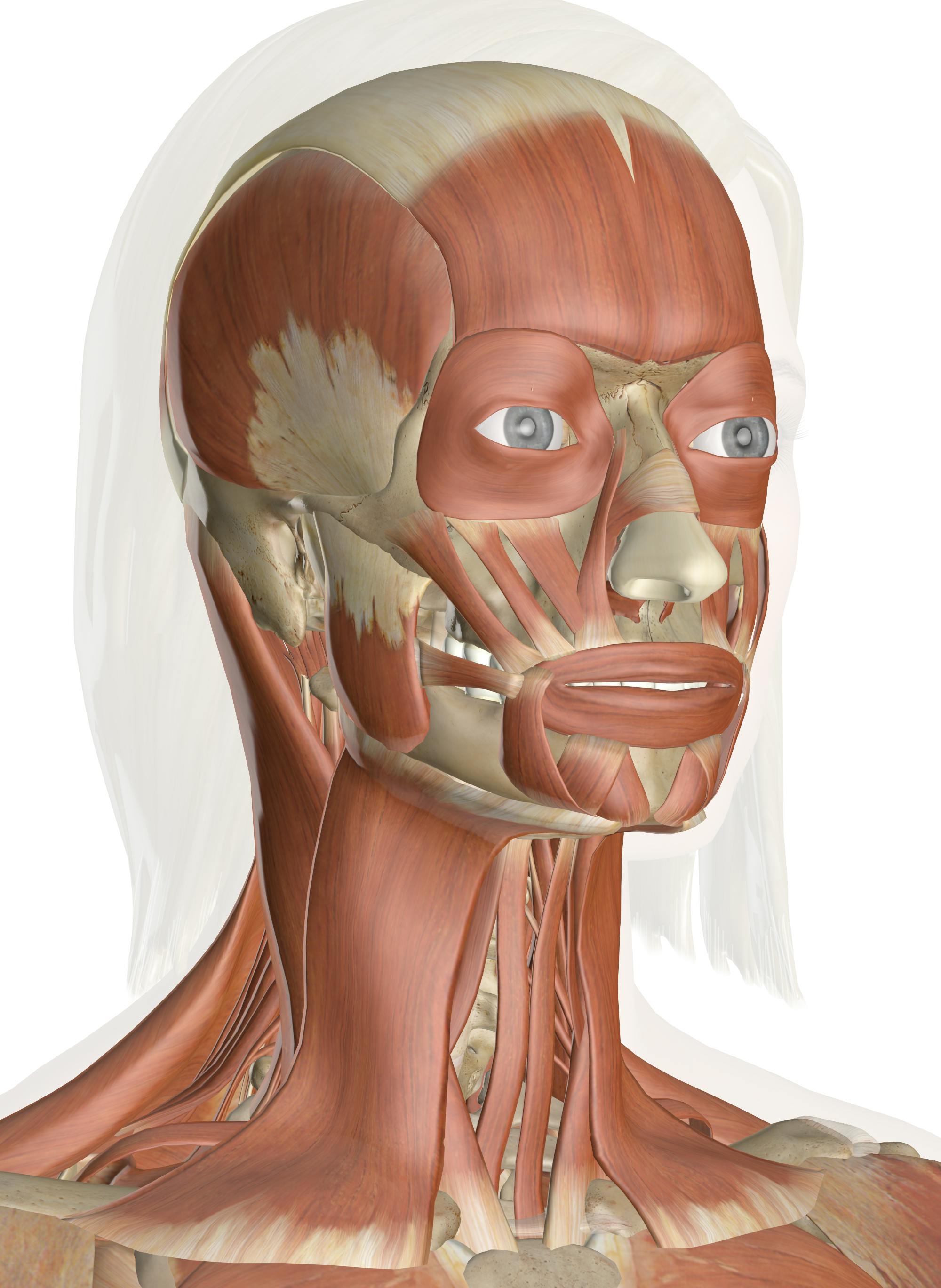



Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information



Anatomy And Physiology Anatomical Position And Directional Terms



Anatomical Terms Wikiradiography




Neck Anatomy Britannica




Chapter 1 Anatomical Terminology Medical Imaging Organ System
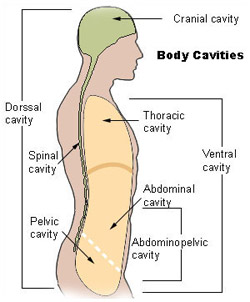



Seer Training Anatomical Terminology
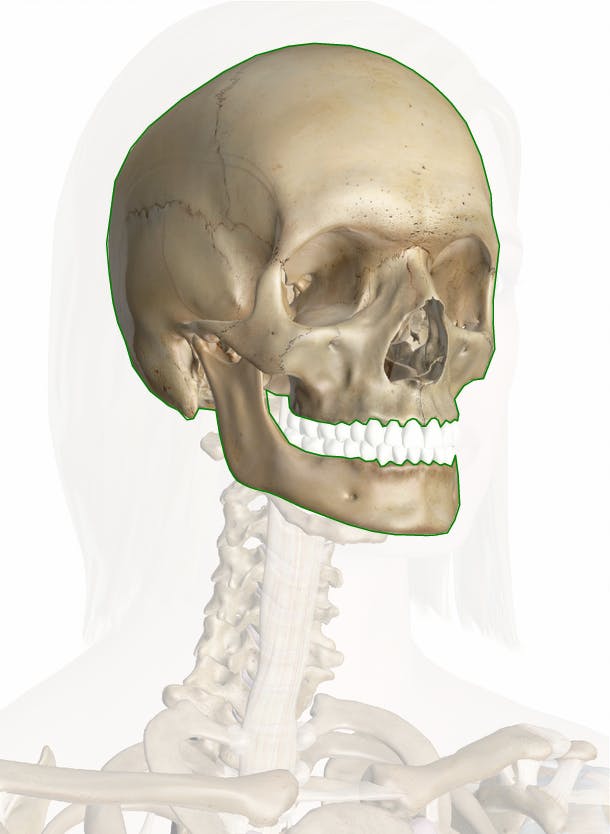



Skull Anatomy Pictures And Information
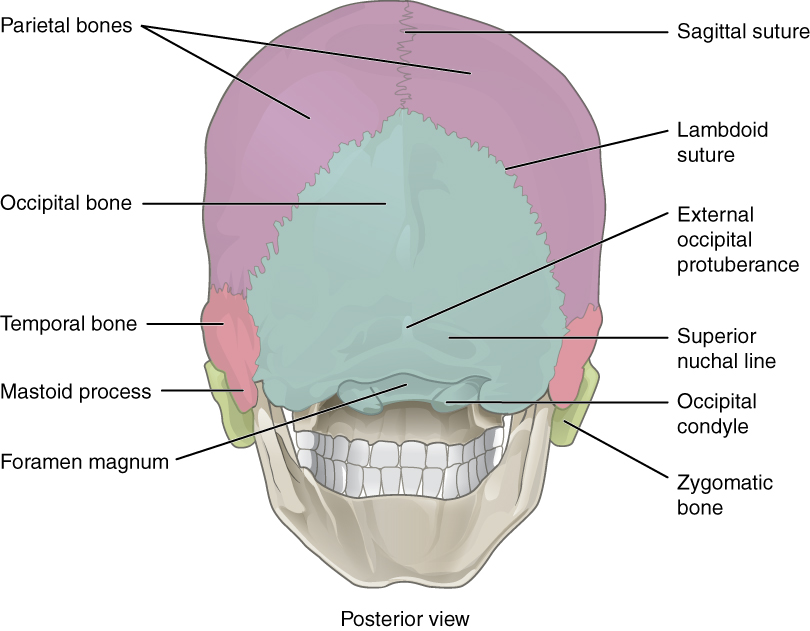



The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
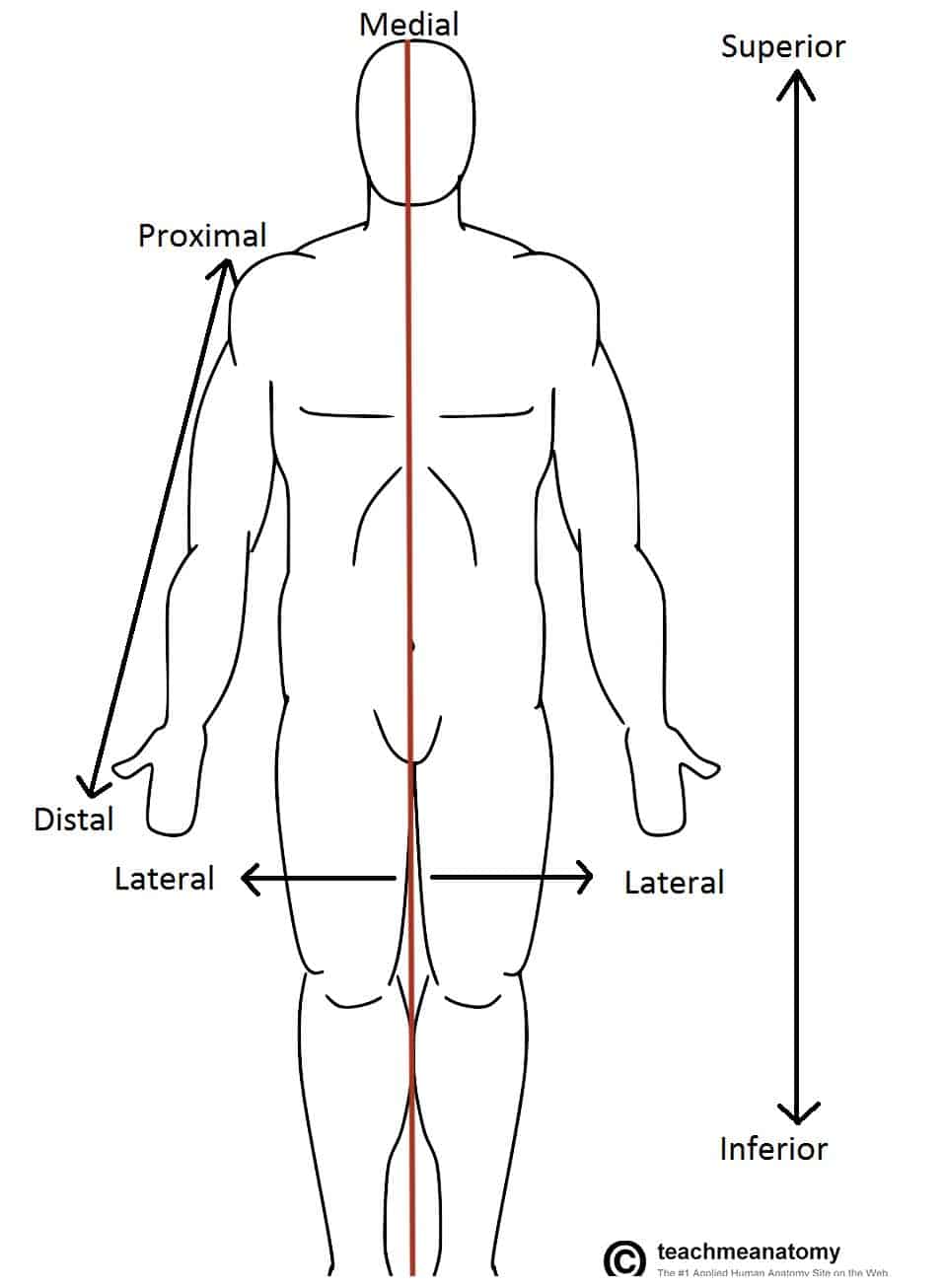



Anatomical Terms Of Location Anterior Posterior Teachmeanatomy




Cranial Cavity Wikipedia
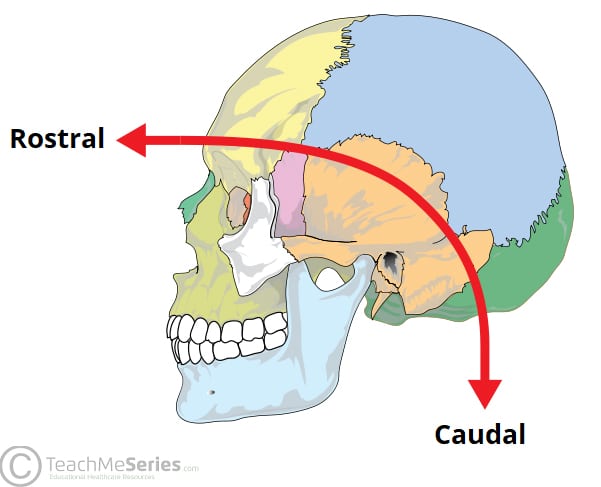



Embryological Terminology Dorsal Ventral Caudal Teachmeanatomy



1




An Introduction To The Human Body Anatomy Science
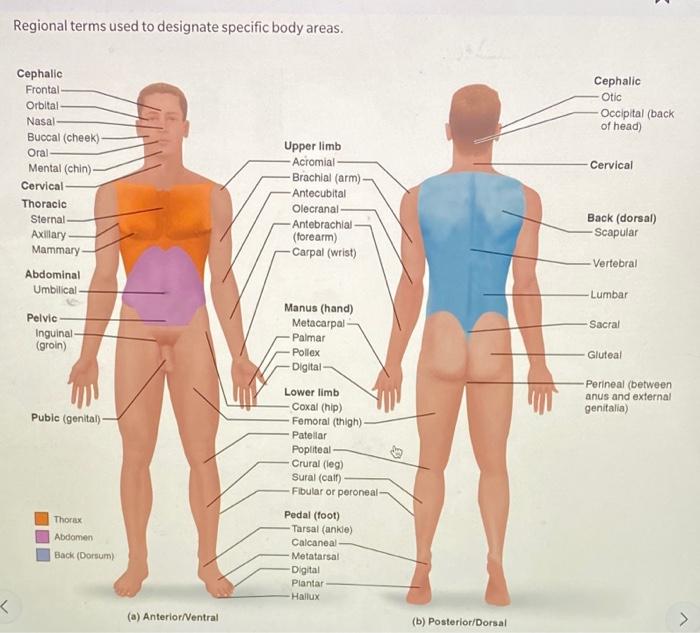



Ii Regional Terms Identify The Following Regions On Chegg Com




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Anatomical Terminology Foundations Of Neuroscience




40 Anatomy Ideas Anatomy Teaching Science Homeschool Science



Anatomy And Physiology Anatomical Position And Directional Terms
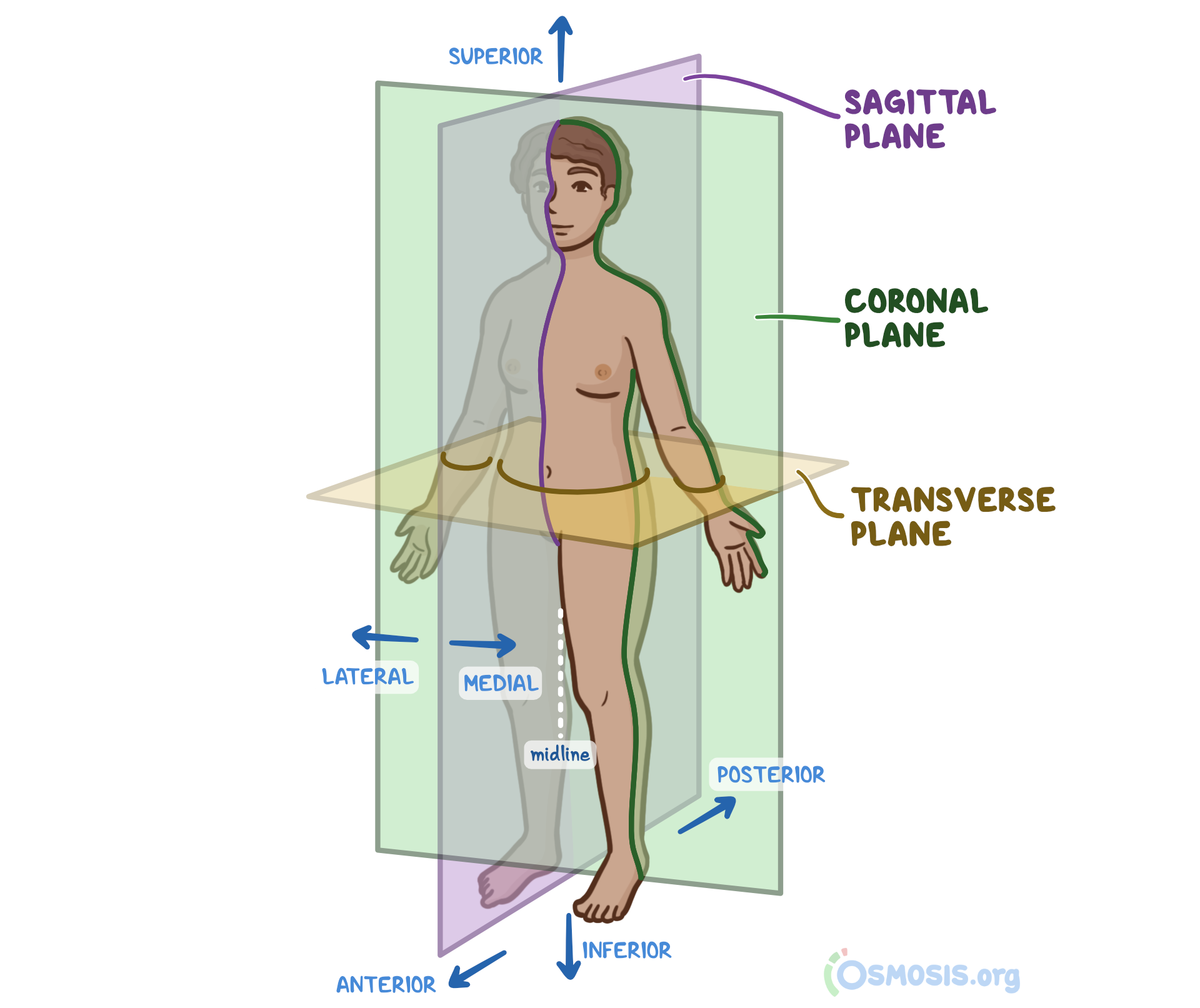



Anatomical Position What Is It Significance Regions Planes And More Osmosis
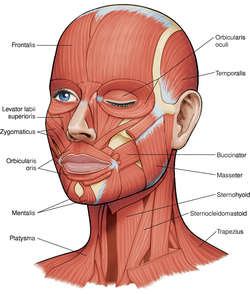



Head Anatomy Definition Of Head Anatomy By Medical Dictionary




1 4 Anatomical Terminology Anatomy Physiology




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck




Anatomical Terminology Anatomy And Physiology I




Anatomical Positions Ppt Video Online Download




Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy And Physiology




Anatomical Directional Terminology Anterior Posterior And More Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
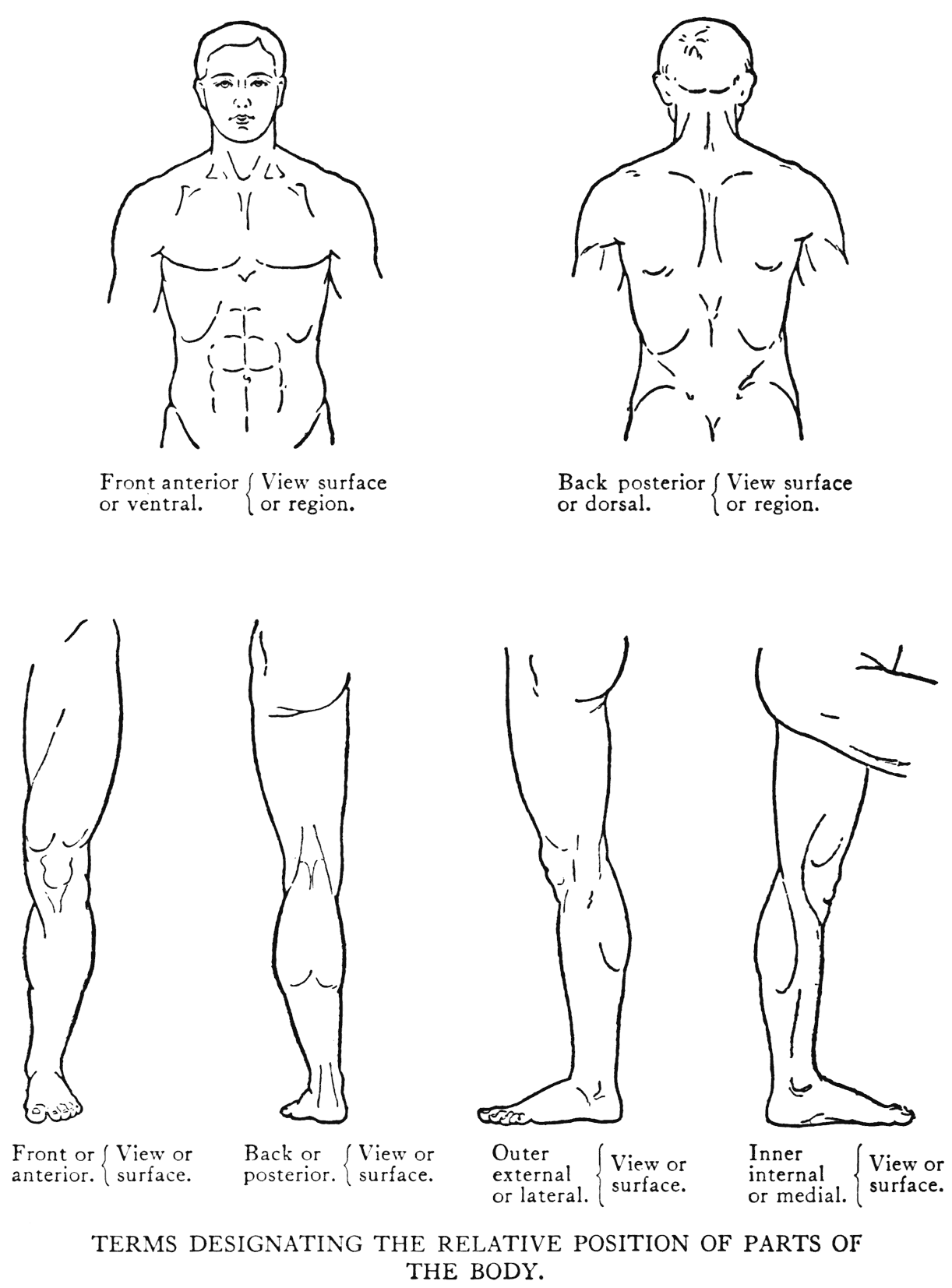



Practical Art Anatomy E G Lutz




Human Head Wikipedia




File Anatomical Terminology Enko Svg Wikimedia Commons




Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy And Physiology
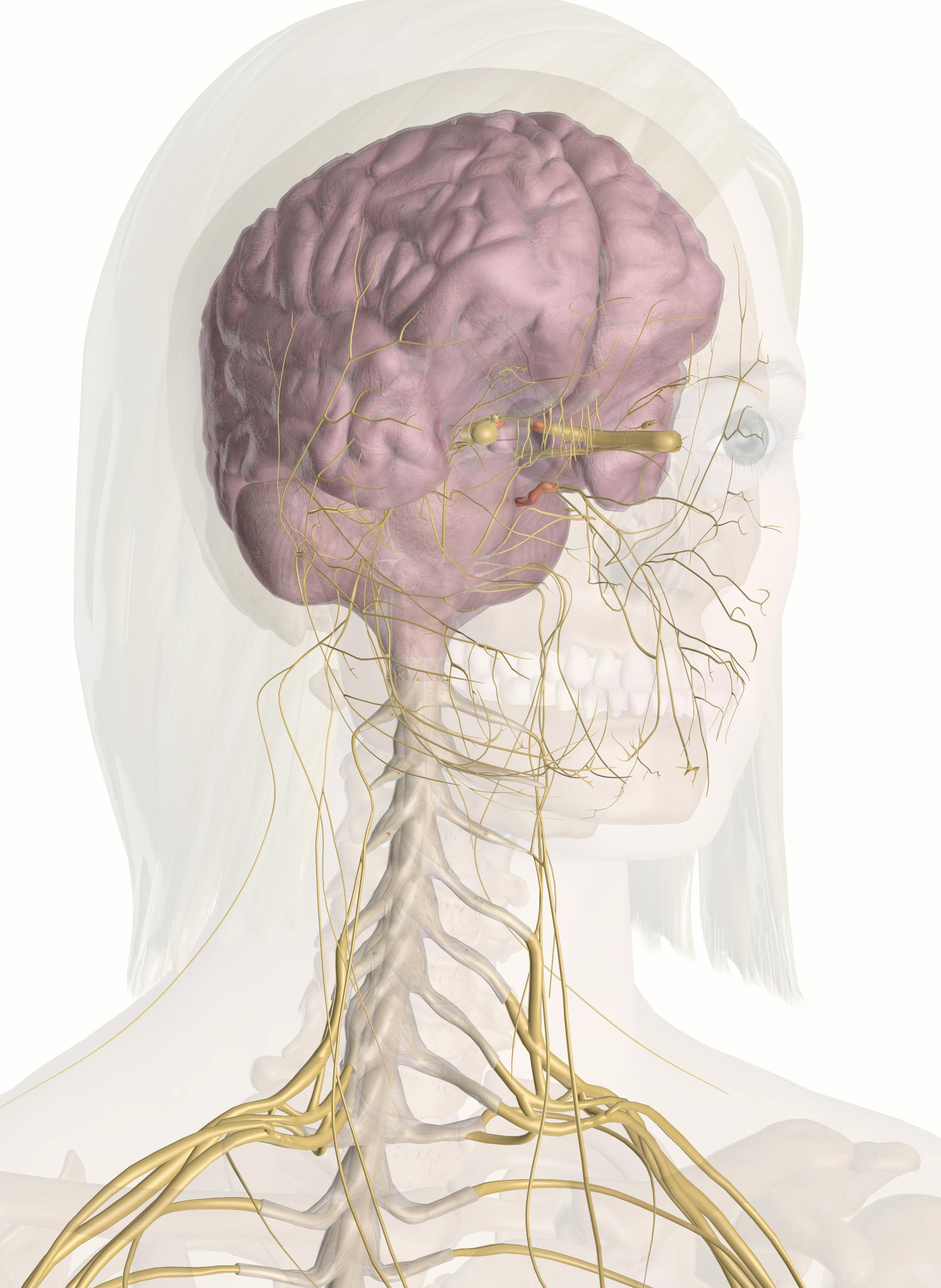



Nerves Of The Head And Neck Interactive Anatomy Guide




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Posterior Anatomical Terms Diagram Quizlet
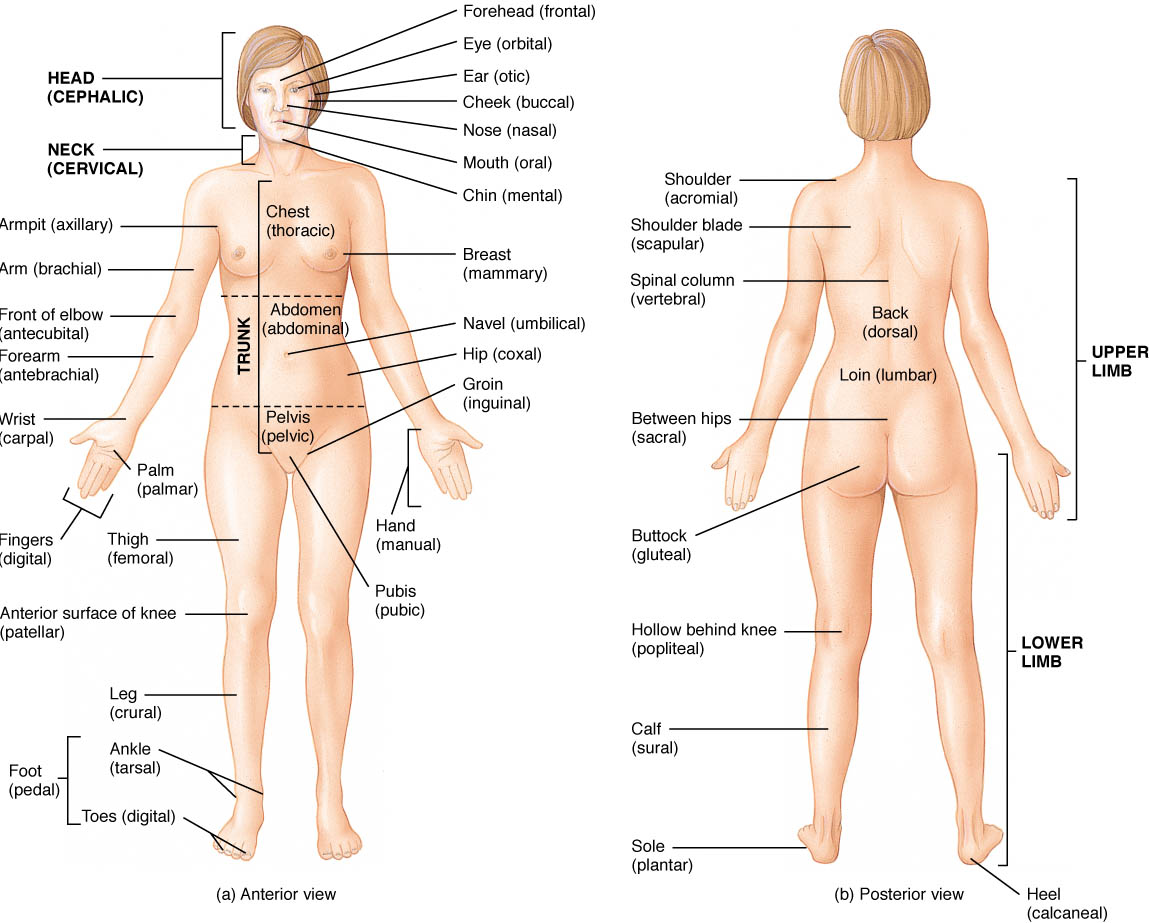



The Language Of Anatomy Anatomical Position And Directional Terms Anatomy Physiology



3




Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica




Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



コメント
コメントを投稿